Machine Learning in Action : เริ่มต้นด้วยเกมเล็กๆอย่าง Tic Tac Toe
มีไอเดียอยากลองทำเกมง่ายๆ ที่สามารถเรียนรู้ หรือพัฒนาตนเองได้ด้วยประสบการณ์ที่ตัวมันได้พบเจอมา ซึ่งมันก็มีหลายเทคนิคที่มีใช้กันอยู่ และที่เห็นว่าน่าสนใจก็เป็น Q-Learning และ Minimax ทั้งสองเทคนิคล้วนแล้วแต่เป็น State–Action–Reward–State คือ เริ่มต้นคิดจาก State ปัจจุบัน เพื่อหา Action และประเมินผลเป็น Reward จาก State อีกที ซึ่งเหมาะสมมากที่จะนำมาใช้ในระบบเกม
ส่วนเกมที่สนใจจะนำมาทดลองนั้น ก็เป็นเกมง่ายๆ อย่างเกม Tic Tac Toe ที่มีรูปแบบไม่เยอะมากนัก กฎกติกาไม่ซับซ้อน และเป็นการแข่งขันกันของสองผู้เล่น ทำให้ระบบสามารถเรียนรู้ หรือเลียนแบบ วิธีการเล่นของฝั่งตรงข้ามได้โดยง่าย ผ่าน State ที่ได้บันทึกไว้ก่อนหน้านี้เท่านั้นเอง
ข้อเสียของวิธีการใช้ State แบบนี้คือ รูปแบบในการเล่นมักจะถูกจำกัดอยู่เฉพาะจากประสบการณ์ที่ผ่านมาเท่านั้น แม้จะเป็นการเลือกวิธีการเล่นที่ดีที่สุด แต่ก็จะดีที่สุดเท่าที่รู้อยู่เท่านั้น ดังนั้นถ้าประสบการณ์ของมันเต็มไปด้วยวิธีการที่ไม่มีคุณภาพ หรือไร้ประสิทธิภาพแล้ว ตัวมันก็เองก็จะมีพฤติกรรมที่ด้อยคุณภาพไปด้วยเช่นกัน
เริ่มต้นออกแบบ
เราจะแบ่งระบบออกเป็น 3 ส่วนใหญ่ๆ ดังนั้น
- ส่วนของระบบเกม การจัดการแสดงตาราง การจัดการ Turn ของผู้เล่น รับค่า Input จากคีย์บอร์ด การกำหนดผู้เริ่มเล่น
- ส่วนของการตัดสินเกม ระบบนี้จะทำงานเมื่อเกมสิ้นสุดลง และตัดสินผลของเกม
- ส่วนของตัว Machine ที่สามารถเรียนรู้ และตัดสินใจในการเล่นแข่งขันกับผู้เล่นที่เป็นมนุษย์
ระบบเกมส์
เริ่มที่การกำหนดวิธีการเล่น และการใช้งานของเกมส์นี้
โดยเราจะเล่นผ่าน Console Terminal เป็นหลัก เพื่อลดภาระงานการออกแบบ Graphic ที่ไม่ใช่จุดประสงค์หลักของสิ่งที่เรากำลังจะทำนี้ ทำให้สภาวะแวดล้อมของเกมส์จะมีลักษณะประมาณนี้ครับ
- พื้นที่ในเกมส์ จะเป็นตารางขนาด 3×3 ช่อง รวมแล้วมี 9 ช่อง: กำหนดให้ค่า 1 – 9 แทนตำแหน่งของแต่ละช่องของตาราง
- สถานะของแต่ละช่อง มี 3 สถานะ คือ X , O และ ว่าง: กำหนดให้ X มีค่าเป็น 1 , O มีค่าเป็น -1 และสถานะว่างมีค่าเป็น 0 เพื่อให้สามารถทำการคำนวณทางคณิตศาสตร์ได้ง่ายมากขึ้น
- กำหนดให้ X เป็นผู้เริ่มเล่นก่อนเสมอ เพื่อให้ง่ายต่อการสร้าง State ให้กับบอต
- มีการคำนวนส่วนตัดสินเกมทุกครั้งที่จบ Turn
- แสดงตารางในสภาวะปัจจุบันหลังจบ Turn
การตัดสินเกม
ใช้ผลรวมของผลสัมบูรณ์ในแต่ละหลัก ถ้าหากเท่ากับ 3 ก็จะถือว่ามีผู้ชนะ
แต่หากไม่มีผู้แพ้ชนะ และไม่มีช่องตารางว่างเหลืออยู่แล้ว ก็จะให้ผลเสมอ
นอกจากเงื่อนไขนี้จะถือว่าเกมยังไม่จบลง
- คำนวนผลจากตาราง ณ ปัจจุบัน
- ให้ผลว่าใครเป็นผู้ชนะ เมื่อ X เป็นผู้ชนะ ให้ผล 1 , เมื่อ O เป็นผู้ชนะ ให้ผล -1 , เสมอให้ผลเป็น 0 และถ้าเกมส์ยังไม่จบ ให้ผล None เพื่อให้ระบบเกมทำงานต่อไป
ระบบ Machine
ใช้ วิธี Minimax ในการประเมินสถานการณ์และตัดสินใจว่า Machine ควรจะตอบสนองต่อสถานการณ์นั้นอย่างไร
- บันทึกตารางในแต่ละสถานะ
- สร้างความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างสถานะ
- คำนวนค่าความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างสถานะ
- ตัดสินใจเลือกการกระทำจากค่าความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างสถานการณ์ปัจจุบันกับสถานะถัดไป
- เมื่อไม่มีสถานะที่เหมาะสม ให้ทำการสุ่มเล่น
ระบบตัดสินเกม
เป็นฟังก์ชันง่ายๆ ที่เริ่มโดยรับค่าตาราง ณ เวลาปัจจุบันเข้ามา
เริ่มต้นตรวจสอบว่ามีช่องว่างเหลืออยู่บนตารางหรือไม่
1 2 3 | for i in range(9): if game_state[i] == 0: draw_flag = 1 |
แล้วคำนวนตามแกนต่างๆ ว่ามีแกนใดที่มีหมากของผู้เล่นวางเรียงกัน ทำให้มีผลรวมของค่าสัมบูรณ์แล้วเท่ากับ 3 บ้าง ถ้าหากมีก็ส่งค่าของผู้ชนะกลับไป
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | if (abs(game_state[0] + game_state[1] + game_state[2]) == 3): return game_state[0], "Done" if (abs(game_state[3] + game_state[4] + game_state[5]) == 3): return game_state[3], "Done" if (abs(game_state[6] + game_state[7] + game_state[8]) == 3): return game_state[6], "Done" if (abs(game_state[0] + game_state[3] + game_state[6]) == 3): return game_state[0], "Done" if (abs(game_state[1] + game_state[4] + game_state[7]) == 3): return game_state[1], "Done" if (abs(game_state[2] + game_state[5] + game_state[8]) == 3): return game_state[2], "Done" if (abs(game_state[0] + game_state[4] + game_state[8]) == 3): return game_state[4], "Done" if (abs(game_state[2] + game_state[4] + game_state[6]) == 3): return game_state[4], "Done" |
แต่หากว่ายังไม่มีผู้ชนะ แต่ไม่มีช่องว่างบนตารางเหลืออยู่แล้ว จะถือว่าเกมนี้จบลงด้วยผลเสมอ ค่าที่ส่งคือ 0
1 2 | if draw_flag is 0: return 0, "Done" |
ถ้าหากยังไม่มีสถานการณ์ที่เป็นไปตามเงื่อนไขใดเลย ถือว่าเกมยังสิ้นสุดจะส่งค่า None
1 | return None, "Not Done" |
นี่คือฟังก์ชันที่เราจะใช้ตรวจสอบ และตัดสินเกม Tic – Tac – Toe ของเราครับ
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | def check_current_state(game_state): draw_flag = 0 for i in range(9): if game_state[i] == 0: draw_flag = 1 if (abs(game_state[0] + game_state[1] + game_state[2]) == 3): return game_state[0], "Done" if (abs(game_state[3] + game_state[4] + game_state[5]) == 3): return game_state[3], "Done" if (abs(game_state[6] + game_state[7] + game_state[8]) == 3): return game_state[6], "Done" if (abs(game_state[0] + game_state[3] + game_state[6]) == 3): return game_state[0], "Done" if (abs(game_state[1] + game_state[4] + game_state[7]) == 3): return game_state[1], "Done" if (abs(game_state[2] + game_state[5] + game_state[8]) == 3): return game_state[2], "Done" if (abs(game_state[0] + game_state[4] + game_state[8]) == 3): return game_state[4], "Done" if (abs(game_state[2] + game_state[4] + game_state[6]) == 3): return game_state[4], "Done" if draw_flag is 0: return 0, "Done" return None, "Not Done" |
ระบบเกม
ฟังก์ชันการแสดงผลตาราง
เนื่องจากในระบบ เราต้องการให้ระบบสามารถคำนวณผลได้โดยง่าย บันทึกตารางการเล่นสำหรับให้ Machine ได้เรียนรู้ได้ง่ายขึ้น เราจึงเก็บตารางในรูปแบบ List ขนาด 9 ช่อง
และใช้ตัวเลขแทนสถานะบนตาราง
แต่มันจะยุ่งยากเกินไปถ้าหากนำตารางแบบนั้นมาแสดงเพื่อการใช้งาน ดังนั้นจึงต้องสร้างการแสดงผลขึ้นมาใหม่ เพื่อให้ง่ายต่อการใช้งานมากขึ้น โดยเราอยากได้การแสดงผลตารางอยู่ในรูปแบบนี้
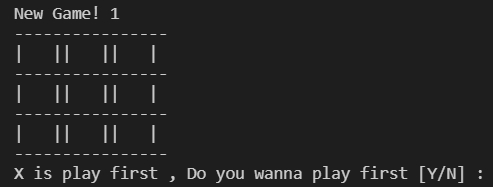
เพื่อความสะดวก จึงสร้างเป็นฟังก์ชันง่ายๆ ขึ้นมา เพื่อใช้ในการแสดงตารางแทน
โดยการแทนค่าตัวเลขที่อยู่ในลิสต์ ด้วยตัวอักษร X , O และช่องว่าง ในตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้องแล้วนำมันมาแสดงผล
ตัวแปร List สำหรับเก็บค่าไว้แสดงผล
1 2 3 | show_state = [ ' ',' ',' ', ' ',' ',' ', ' ',' ',' ' ] |
วนแทนค่าจากตารางในระบบ ให้เป็นตารางสำหรับแสดงผล
1 2 | for pos in range(len(game_state)): show_state[pos] = dict_state[game_state[pos]] |
ส่วนแสดงผลผ่าน Terminal
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | print('----------------') print('| {} || {} || {} |'.format(show_state[0],show_state[1],show_state[2])) print('----------------') print('| {} || {} || {} |'.format(show_state[3],show_state[4],show_state[5])) print('----------------') print('| {} || {} || {} |'.format(show_state[6],show_state[7],show_state[8])) print('----------------') |
ฟังก์ชันรับค่าจากคีย์บอร์ด
ฟังก์ชันนี้จะรับค่าตำแหน่ง 1 – 9 จากคีย์บอร์ด และตรวจสอบว่าค่าที่ได้รับเหมาะสมและใช้งานได้หรือไม่ ก่อนที่จะส่งค่าตำแหน่งที่เล่นคืนกลับสู่ระบบเกม เพื่อให้เกมดำเนินต่อไป
ส่วนการตรวจสอบช่องว่างบนตารางที่สามารถเล่นได้
1 2 3 4 | for pos in range(len(state)): if state[pos] == 0: aval_block.append(pos+1) print("get aval_block : {}".format(aval_block)) |
ส่วนของการวนรับค่า และตรวจสอบข้อมูลที่ได้รับว่าใช้งานได้หรือไม่
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | while cont: blockInput = input("Human !!!! , your turn! Choose where to place {} to {}: ".format(dict_state[playas],aval_block)) if blockInput.isdigit(): block_choice = int(blockInput) if block_choice not in aval_block: print("Please insert only {}".format(aval_block)) else: play_block = block_choice cont = False |
ฟังก์ชันการเคลียร์ Terminal
ใช้เพื่อล้างข้อความที่แสดงอยู่บน Terminal เพื่อให้สามารถแสดงข้อความอื่นขึ้นมาแทนที่ได้ ซึ่งคำสั่งล้างข้อความนี้ บนระบบวินโดวส์กับลินุกส์ จะใช้คำสั่งแตกต่างกันครับ
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | # define our clear function def scnclear(): # for windows if name == 'nt': _ = system('cls') # for mac and linux(here, os.name is 'posix') else: _ = system('clear') |
ฟังก์ชันการอัปเดตตาราง
เพราะระบบของเกมจะต้องรองรับทั้งค่าที่ได้รับจากคีย์บอร์ด และค่าที่ได้จาก Machine
ดังนั้นจึงทำฟังก์ชันขึ้นมา เพื่อให้ทั้งสองวิธีสามารถส่งผ่านตำแหน่งการเล่นของตนไปสู่ตารางเดียวกันได้
1 2 3 | def play_move(state, player, block_num): if state[int(block_num-1)] == 0: state[int(block_num-1)] = dict_player[player] |
ระบบเกมหลัก
เกมจะเริ่มต้นที่ การเลือกว่าจะให้ Machine เล่นกับใคร โดยมี 3 ตัวเลือกคือ
- You VS Machine
- Random VS Machine
- Machine VS Machine
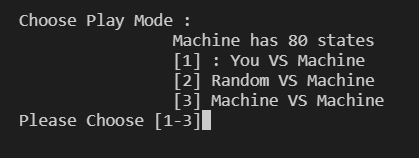
โค้ดส่วนการเลือก Mode ของเกม ซึ่งจะวนถาม/รับค่า ไปจนกว่าคำตอบนั้นจะเหมาะสมกับตัวเลือกที่มีให้
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | while play_mode not in pMode: print('''Choose Play Mode : Machine has {} states [1] : You VS Machine [2] Random VS Machine [3] Machine VS Machine'''.format(len(mk.state_action))) play_mode = input("Please Choose [1-3]") print("PlayMode : {}".format(play_mode)) |
เมื่อเลือก Mode เรียบร้อย เกมจะให้เราเลือกว่า เราจะเป็นฝ่ายเริ่มก่อนหรือไม่
ถ้าเราจะเริ่มเล่นก่อนให้ตอบ Y แล้วกด Enter

โค้ดที่ใช้รับค่าและตรวจสอบค่าที่ได้รับ ซึ่งจะทำงานก็ต่อเมื่อเราเล่นใน Mode ในข้อ 1 เท่านั้น
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | print("New Game! {}".format(playCount)) print_board(game_state) if play_mode == '1': player_choice = input("X is play first , Do you wanna play first [Y/N] : ") winner = None if player_choice == 'Y' or player_choice == 'y': # player_choice = 'X' mk.playFirst = False else: # player_choice = 'O' mk.playFirst = True |
โค้ดในส่วนที่ใช้จัดการลำดับการเล่นของผู้เล่นในแต่ละ Turn
โดยมีตัวแปล current_player เป็นตัวกำหนดว่ารอบเป็น Turn ของ X หรือ O
และในแต่ละ Turn จะถูกจัดการตาม Mode ที่ได้เลือกไว้ก่อนหน้านี้
ตารางจะอัพเดทผ่านฟังก์ชัน play_move ที่ถูกสร้างไว้ก่อนหน้า
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | while current_state == "Not Done": print("current game_state : {}".format(game_state)) if current_player == 1: # play X if play_mode == '1': if mk.playFirst: block_choice = AI_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) else: block_choice = Human_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) elif play_mode == '3': block_choice = AI_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) else: if mk.playFirst: block_choice = AI_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) else: block_choice = random_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) else: # play O if play_mode == '1': if not mk.playFirst: block_choice = AI_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) else: block_choice = Human_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) elif play_mode == '3': block_choice = AI_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) else: if not mk.playFirst: block_choice = AI_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) else: block_choice = random_turn(state = game_state, playas = current_player) play_move(game_state ,dict_state[current_player], block_choice) |
ส่วนถัดมาจะเป็นส่วนของการแสดงผลและตรวจสอบเพื่อตัดสินเกม
โดยจะเริ่มที่การเคลียร์ Terminal เพื่อให้สามารถแสดงผลตารางใหม่ลงไปได้
แล้วค่อยตรวจสอบเพื่อตัดสินเกมว่าเกมนี้สิ้นสุดลงหรือยัง มีผู้ชนะหรือไม่
ถ้าหากเกมจบลงแล้ว ระบบก็จะทำการรายงานผลบน Terminal ข้างล่างตารางต่อไป
และปิดท้ายด้วยการอัปเดตสถานะเพื่อให้ Machine ได้เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมจากเกมนี้
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 | scnclear() print("Game! {}".format(playCount)) # print("current game_state : {}".format(game_state)) print_board(game_state) winner, current_state = check_current_state(game_state) if winner is not None: if winner == 1: winbyX +=1 print("Game! {} - {} won!".format(playCount, dict_state[winner])) elif winner == -1: winbyO +=1 print("Game! {} - {} won!".format(playCount, dict_state[winner])) else: Draw +=1 print("Game! {} - Draw!".format(playCount)) winRateX = float(winbyX/playCount) winRateO = float(winbyO/playCount) drawRate = float(Draw/playCount) mk.updateResult(winner) print("playCount : Winby X : Winby O : Draw --- {} : {:05.3f} : {:05.3f} : {:05.3f}".format(playCount,winRateX,winRateO,drawRate)) print("AI State has : {}".format(len(mk.state_action))) print("AI Stat has {}".format(mk.resultStat)) mk.update_state_action(game_state,winner) mk.save_state_action() time.sleep(3) else: current_player *= -1 mk.update_state_action(game_state,0) |
หลังจบเกมในกรณีที่เลือก Mode 1 จะมีการถามว่า ยังจะเล่นต่ออีกหรือไม่
และใน Mode 2 จะมีการสลับกันเล่นของ Machine กับการเล่นแบบสุ่ม
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | if play_mode == '1': play_again = input('Lets Play Again?(Y/N) : ') elif play_mode == '2': mk.playFirst = not mk.playFirst play_again = 'Y' else: play_again = 'Y' |
ระบบ Machine
กระบวนการตัดสินใจของ Machine
แนวคิดของ Minimax หรือ Q-Learning นั้น มีการใช้ State เพื่อกำหนด Action โดยเลือกจาก Reward ที่เหมาะสมที่สุดจากความสัมพันธ์ของ State กับ State
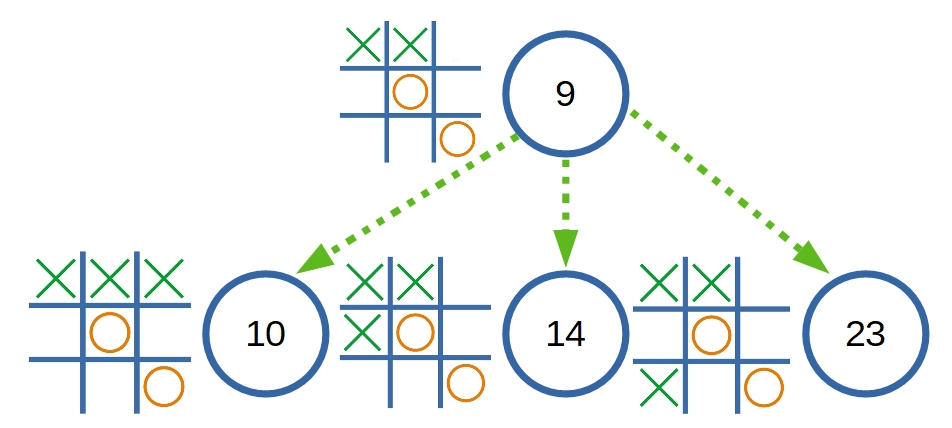
ซึ่งในตัวอย่าง ณ ปัจจุบัน เป็น State ที่ 9 ซึ่งนั่นคือสถานะที่เกิดจากการเล่นของอีกฝั่ง ใน Turn ของ Machine ดังที่เห็นว่า Machine เรียนรู้มามีเพียง 3 ทางเลือกเท่านั้น
สิ่งสำคัญคือ ต้องทำให้ Machine รับรู้ได้ว่า แต่ละเส้นทางของทั้ง 3 ทางเลือกนั้น ทางเลือกใดเหมาะสมที่สุด ในวิธี Minimax นั้น จะใช้ขนาดของคะแนนเป็นเกณฑ์ในการตัดสินใจ ว่าจะเลือกเส้นทางใด ดังนั้นเราจึงต้องสร้างกระบวนการประเมินคะแนนให้กับแต่ละ State ที่ Machine สามารถเลือกได้
การคำนวนคะแนน Reward
เงื่อนไขของคะแนนที่จะต้องมีคือ
- จะต้องแยกได้ว่าใครแพ้ ใครชนะ และเสมอได้ เพราะ Machine จะต้องเลือกทางที่ตนมีโอกาสชนะมากที่สุด หรือดักทางที่ตนมีโอกาสมากที่สุด
- ขนาดคะแนนจะต้องลดความสำคัญลงตามความลึกของลำดับการเล่นได้ เพื่อให้สามารถเปรียบเทียบได้ว่า Machine หรือ คู่ต่อสู้ จะเป็นผู้ชนะก่อนในเส้นทางนั้น
จากระบบเกมส์ที่เก็บค่าบนตารางด้วยการใช้ค่า 1 , 0 และ -1 แทนพื้นที่บนตาราง
จึงมองว่าก็สามารถเอาค่านั้นมาเป็น Reward หรือคะแนน เพื่อแทนสักษณะของสถานการณ์นั้นได้เช่นกัน เช่นถ้าหากว่า X เป็นผู้ชนะ Reward ก็จะมีค่าเป็น 1 เหมือนกับที่ระบบเกมใช้ 1 แทน X บนตาราง หรือหาก O เป็นผู้ชนะ Reward จะมีค่าเป็น -1 และหากผลคือเสมอ Reward จะมีค่าเป็น 0
และลำดับชั้นที่อยู่ถัดขึ้นไปจากสถานะนั้น Reward ก็จะถูกลดทอนลงด้วยค่า Discount ไปเรื่อยๆ ดังนั้น ยิ่งสถานะ แพ้ – ชนะ อยู่ลึกลงไปจากสถานะปัจจุบันมากเท่าไร คะแนนก็จะมีผลสัมบูรณ์ลดลงไปเรื่อยๆ ดังนั้นจากคะแนนของแต่ละ State ก็จะทำให้ Machine มองเห็นว่า แต่ละ State ให้ผลอย่างไรในอนาคต เป็นประโยชน์ต่อตนเองมากแค่ไหน
การเปรียบเทียบคะแนน
สิ่งสำคัญอีกอย่างในการตัดสินใจคือ การเปรียบเทียบคะแนน
ในกรณีนี้เลือกที่จะใช้ผลสัมบูรณ์ที่มากที่สุดของ State ที่สัมพันธ์กันกับ State ปัจจุบัน แล้วคูณด้วยค่า Discount เพื่อลดทอนลงตามลำดับชั้นที่สูงขึ้น มาเป็นคะแนนของ State นี้
เหตุที่ใช้ค่าสัมบูรณ์ เนื่องจากว่า จะต้องคำนึงถึง State ที่คู่ต่อสู้จะเล่นเพื่อเอาชนะ Machine ด้วย เช่นกรณีตัวอย่างของความสัมพันธ์นี้
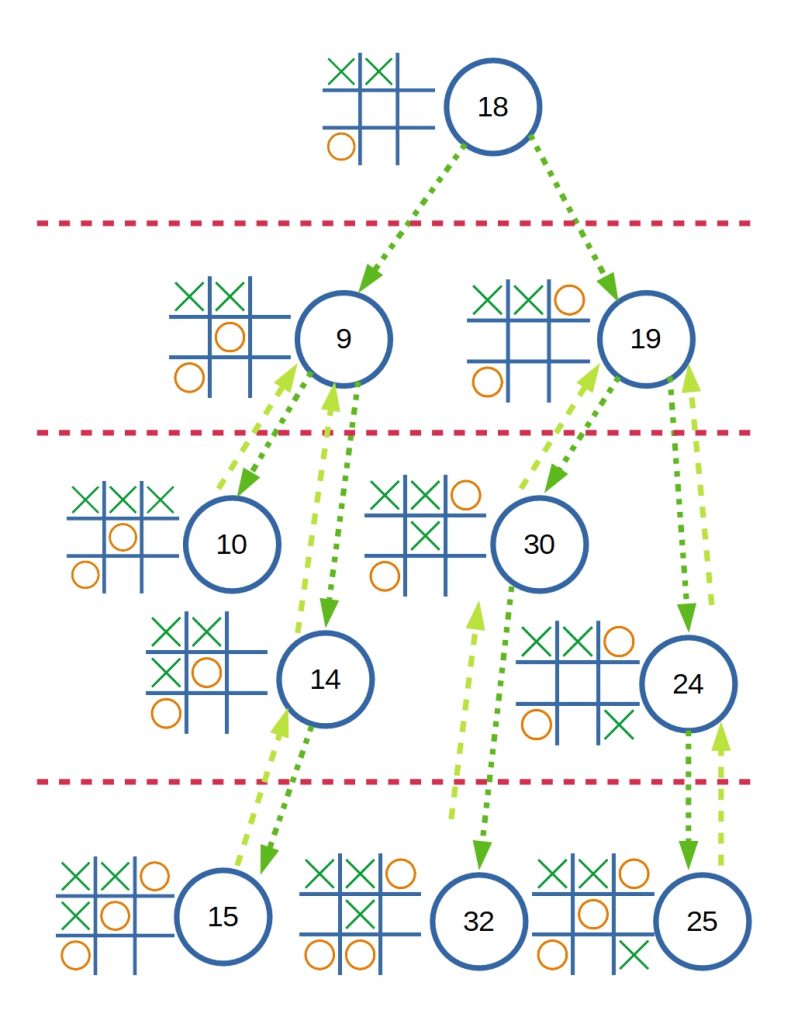
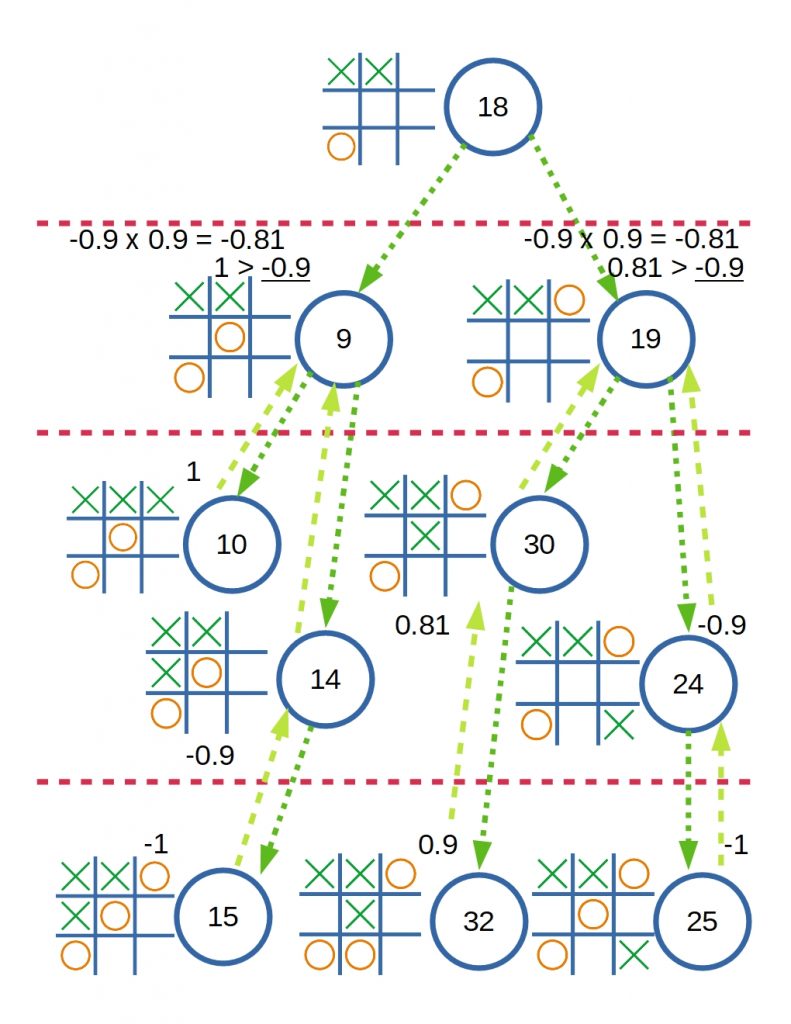
State ที่ 9 นั้น O ไม่ควรเล่นแบบนี้ เพราะ O มีโอกาสแพ้ได้สูงมาก
ถ้าหากว่า State ที่ 10 มี Reward เป็น 1 เนื่องจาก X เป็นผู้ชนะ State ที่ 9 Reward ก็ควรมีค่าเป็น 0.9 หลังจากผ่านการคูณด้วยค่า Discount แล้ว ถ้าหากว่าเราทำการเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใน State อื่นแล้ว 0.9 นี้ก็น่าจะเป็นค่าที่มากที่สุดแล้ว เพราะชัยชนะของ X อยู่ใกล้มาก
แต่ถ้าเราสนใจเลือก State ที่มีคะแนนน้อยที่สุด ซึ่งดูเหมาะสมกับ O ที่มีคะแนนเป็นลบ
เพื่อจะเลี่ยง State ที่ 9 ที่มีคะแนนเป็นบวกได้ และ State 19 ก็ดูจะเหมาะสมกว่า
แต่ถ้าออกแบบให้ระบบส่งคะแนนที่น้อยที่สุดเสมอ เมื่อคำนวนแล้วจะพบว่า State 9 จะไม่มีคะแนนเป็น 0.9 แล้ว เพราะ State 9 มี 2 State สัมพันธ์อยู่ คือ 10 และ 14 ซึ่ง State 14 มีคะแนนน้อยกว่า State 10 ดังนั้น State 14 จะถูกคำนวน และส่งมาเป็นคะแนนของ State 9
ทำให้ Machine อาจจะได้รับข้อมูลที่ผิดไปจากสถานการณ์ และทำให้ตัดสินใจผิดพลาดได้ ตามการคำนวนข้างล่าง
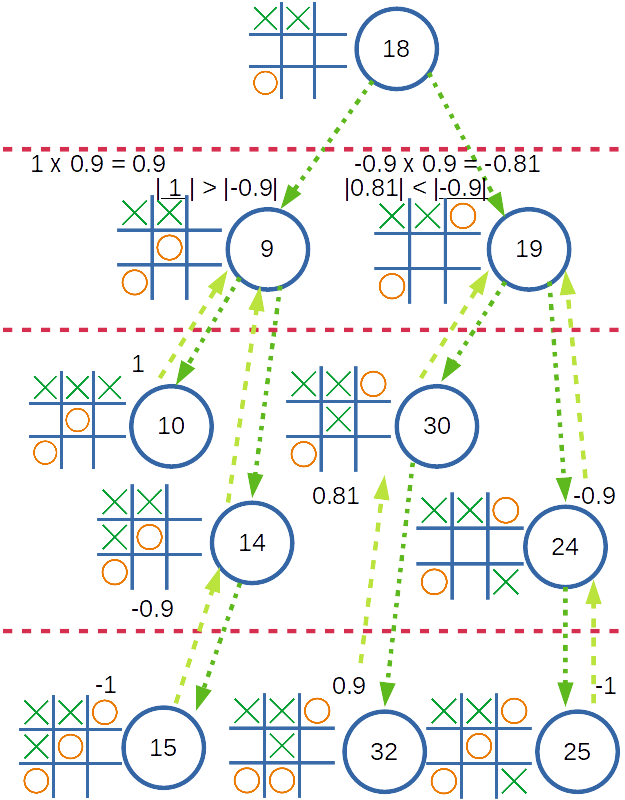
ดังนั้นเราจึงเปลี่ยนแนวคิดใหม่ มาใช้เป็นการเปรียบเทียบจากค่าสัมบูรณ์ที่มากที่สุด แล้วค่อยมาดูว่า แท้จริงค่านั้นเหมือนหรือแตกต่าง จากสิ่งที่ต้องการ เช่นหากว่า Machine เล่นในฐานะ O คะแนนที่มีผลดีที่สุดของ O คือ -1 หรือค่าที่น้อยที่สุด แต่หากว่าเป็น X คะแนนที่มีผลดีที่สุดคือ 1 หรือค่าที่มากที่สุด แต่เพื่อให้ Machine สามารถเอาตัวรอดจากสถานการณ์ตัวอย่างก่อนหน้าได้ Machine จึงต้องประเมินจากการเปรียบเทียบด้วยค่าสัมบูรณ์ ซึ่งจะทำให้ Machine จะต้องเจอสถานการณ์ 2 แบบ นั่นคือ
- แบบแรก คะแนนจริงเป็นผลดีต่อ Machine เช่นเล่นเป็น O ก็มีค่า เป็นลบ หรือเล่นเป็น X คะแนนก็มีค่าเป็น บวก ซึ่ง Machine จะสามารถทำตามสถานการณ์นั้นได้ทันที
- แบบที่สอง คะแนนจริงเป็นผลตรงข้ามต่อ Machine เช่นเล่นเป็น O แต่คะแนนเป็น บวก หรือ เล่นเป็น X แต่คะแนนเป็น ลบ ซึ่งจะเป็นสถานการณ์ที่แย่ที่สุดที่สามารถเกิดขึ้นได้ เท่าที่ Machine รู้จัก
ในกรณีของแบบแรก Machine จะสามารถเล่นตามสถานการณ์นั้นได้ทันที
แต่หากว่าเป็นในกรณีของแบบที่สอง Machine จะต้องเล่นในสถานการณ์ของ State ฝั่งคู่ต่อสู้ ที่อยู่ลึกลงไปอีก 1 ขึ้น เช่น Machine เล่นเป็น O อยู่ใน State 18
สมมติว่า State ที่ 9 คือ State ที่มีค่าสัมบูรณ์สูงที่สุด วิธีที่ Machine จะต้องทำคือ เดินลึกลงไปจาก State ที่ 9 อีก 1 ขั้น ซึ่งมี 2 State คือ 10 และ 14 และเลือกเล่นใน State ที่มีค่าสัมบูรณ์มากที่สุดของ State ที่ 9 นั่นคือ State ที่ 10 ในตำแหน่งการเล่นของ X จะทำให้สถานการณ์กลายมาเป็น State ที่ 19 ไปแทน ซึ่ง O จะยังไม่แพ้โดยง่าย
และถ้าหาก Machine อยู่ใน State ที่ไม่รู้จักล่ะ ในกรณีนี้คงต้องให้ Machine เล่นแบบสุ่มจากช่องบนตารางที่ว่างอยู่ เพื่อเรียนรู้ว่าสถานการณ์แบบนี้เล่นไปแล้วจะให้ผลเช่นไร
สรุปกระบวนการตัดสินใจของ Machine
- รับคะแนน แพ้ ชนะ เสมอ จากผลตัดสินของเกม ใน State สุดท้ายที่เกิดขึ้นนั้น
- เปรียบเทียบคะแนนโดยเลือก State ที่มีผลสัมบูรณ์ของคะแนนที่มากที่สุดเป็นหลัก
- คำนวนคะแนนของ State นั้นโดยคูณกับค่า Discount เพื่อลดทอนคะแนนลงตามความลึกของ State
การทำงานของ Machine
เพื่อให้เกมสามารถเล่นได้ต่อเนื่อง ตัว Machine จำเป็นจะต้องมีการเก็บสถานะไว้ เพื่อให้สามารถนำกลับมาใช้ได้ในครั้งต่อไป ดังนั้นระบบของ Machine จะเริ่มที่การโหลดสถานะที่เก็บไว้ขึ้นมา แล้วจึงเริ่มเกม
ระหว่างที่เกมดำเนินไป นอกจาก Machine จะต้องประเมินสถานการณ์เพื่อเล่นเกมแล้ว
จะต้องมีการเก็บสถานะของเกมไว้เพื่อเพิ่มเป็นประสบการณ์ต่อไป และเมื่อเกมสิ้นสุดจะต้องมีการบันทึกเก็บไว้เพื่อให้สามารถนำกลับมาใช้ได้ในการเล่นครั้งต่อไป
การบันทึกและนำข้อมูลกลับมาใช้ใหม่
ในกรณีนี้เพื่อให้ง่ายต่อการใช้งาน และการตรวจสอบ จึงเลือกที่จะเก็บข้อมูลไว้ใน รูปแบบไฟล์ JSON และข้อมูลสถานะของ Machine จะเก็บในตัวแปรรูปแบบ Dictionary ของ Python ซึ่งสามารถแปลงไปเป็น JSON และแปลงกลับมาได้ไม่ยาก
ฟังค์ชันการดึงข้อมูลกลับมาใส่ตัวแปร state_action ซึ่งชื่อไฟล์ จะถูกตั้งไว้เป็น Default ในตัวแปร state_action_fname
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | def load_state_action(self , fname = None): if fname == None: fname = self.state_action_fname print("current file : {}".format(fname)) flists = open("{}".format(fname), 'r') print("flist was open : {}".format(flists)) dat = flists.read() # print("JSON data : {}".format(dat)) if dat : self.state_action = json.loads(dat) else: self.state_action = {} # print("state_action : {}".format(self.state_action)) |
ฟังค์ชั่นการบันทึกข้อมูล
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | def save_state_action(self , fname = None): if fname == None: fname = self.state_action_fname state_action_json = json.dumps(self.state_action, indent=4) print("current file : {}".format(fname)) flists = open("{}".format(fname), 'w') print("flist was open") flists.write(state_action_json) flists.close() print("flist was closed") |
สำหรับกรณีที่ Machine อยู่ใน State ที่ไม่รู้จัก จะเล่นแบบสุ่ม
ก็จะเลือกใช้ฟังก์ชันนี้ในการเล่นแบบสุ่ม โดยจะสุ่มจากช่องว่างที่มีอยู่บนตาราง
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | def random_next(self , state): aval_block = [] play_block = 0 for pos in range(len(state)): if state[pos] == 0: aval_block.append(pos+1) print("get aval_block : {}".format(aval_block)) play_block = random.choice(aval_block) print("get play_block : {}".format(play_block)) return play_block |
การเก็บ State และสร้างความสัมพันธ์ของ State
Machine จะเก็บ State และผลตัดสินจากระบบ
ซึ่ง Machine จะใช้ State ในการค้นหา โดยจะเปรียบเทียบกับ State ที่มีอยู่ก่อนแล้ว ถ้าหากพบว่ามี State ตรงกับที่มีอยู่แล้ว ค่าลำดับของ State นั้นจะถูกเพิ่มเข้าในส่วนของ ‘next’ ของ State ที่อยู่ในลำดับการเล่นก่อนหน้านั้น เป็นการสร้างความสัมพันธ์ระหว่าง State กัน
แต่ถ้าหาก State นั้น ไม่ปรากฎในข้อมูลที่มีอยู่แล้ว ระบบจะสร้างค่าลำดับใหม่ และนำลำดับนั้นไปเพิ่มเข้าใน ‘next’ ของ State ที่เล่นในลำดับก่อนหน้าเพื่อสร้างความสัมพันธ์ของ State
ถ้าหาก State นั้น มีผลตัดสินแล้ว จะมีการใส่ส่วนของคะแนนลงใน State นั้นด้วย
ส่วนของการค้นหา ผ่านฟังก์ชัน find_state
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | keys_state , value_state = self.find_state(state) if keys_state == '-1': thisState = str("{}".format(len(self.state_action))) thisStateDict = { 'state' : list(state), 'next' : [], 'score' : score_state, 'end' : status_state } self.state_action[thisState] = thisStateDict self.stepList.append(thisState) keys_state = thisState else: self.stepList.append(keys_state) |
ส่วนของการเพิ่ม State ในลำดับการเล่นก่อนหน้า
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | if len(self.stepList) > 1: nxtList = list(self.state_action[self.stepList[-2]]['next']) if keys_state not in nxtList: nxtList.append(keys_state) self.state_action[self.stepList[-2]]['next'] = list(nxtList) # print("state_action : {}".format(self.state_action)) print("stepList : {}".format(self.stepList)) |
โค้ดในส่วนของการอัปเดต State ของ Machine
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | def update_state_action(self , state = None , goal = None): keys_state = '-1' score_state = 0 status_state = False nxtList = [] if (goal == None) or (goal == 0): score_state = 0 else: score_state = goal status_state = True keys_state , value_state = self.find_state(state) if keys_state == '-1': thisState = str("{}".format(len(self.state_action))) thisStateDict = { 'state' : list(state), 'next' : [], 'score' : score_state, 'end' : status_state } self.state_action[thisState] = thisStateDict self.stepList.append(thisState) keys_state = thisState else: self.stepList.append(keys_state) if len(self.stepList) > 1: nxtList = list(self.state_action[self.stepList[-2]]['next']) if keys_state not in nxtList: nxtList.append(keys_state) self.state_action[self.stepList[-2]]['next'] = list(nxtList) # print("state_action : {}".format(self.state_action)) print("stepList : {}".format(self.stepList)) |
การคำนวณคะแนนของแต่ละ State
รูปแบบการทำงาน จะใช้เป็นแบบ Recursive Function ซึ่งจะวนเรียกตัวฟังก์ชันตามจำนวนของ State ที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับ State ที่เป็นปัจจุบัน ลงไปทีละ State จนสุด
ซึ่งจะทำให้ระบบสามารถประเมินคะแนนของทุก State ที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับ State ปัจจุบันได้อย่างถูกต้อง
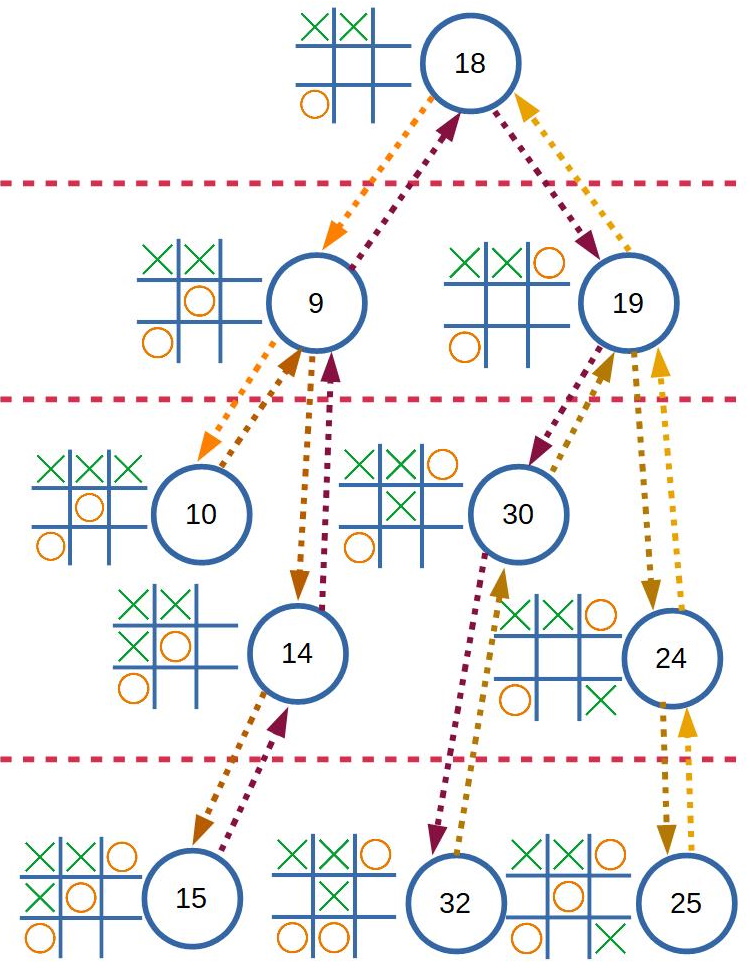
ตัวอย่างการทำงานของฟังก์ชัน ตามลูกศร เริ่มที่ลูกศรสีส้มจาก State 18 ไปยัง State 9 จากซ้ายไปขวา
โค้ดในฟังก์ชันที่ใช้ในการเรียกตัวเอง เพื่อทำงานตาม State ที่สัมพันธ์กับ State นั้นๆ
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | if (currentStep == '-1') or (playas == 0): return '-1' , 0 , False stepIsEnd = self.state_action[currentStep]['end'] if stepIsEnd : currentScore = self.state_action[currentStep]['score'] else : listStep = list(self.state_action[currentStep]['next']) # print("score_calculate currentStep : {} get listStep : {}".format(currentStep,listStep)) for stp in listStep: # print("score_calculate currentStep : {} get stp : {}".format(currentStep, stp)) byStep , stepScore , status = self.score_calculate(stp , playas*(-1)) dictScore[byStep] = { 'score' : stepScore, 'status' : status } print("score_calculate get byStep : {}, stepScore : {:7.4f}, status : {}".format(currentStep , stepScore , status)) self.listEdge.append(tuple([currentStep,byStep,abs(stepScore)])) # print("score_calculate playas : {} currentStep : {} get dictScore : {}".format(playas, currentStep,dictScore)) |
ส่วนของการประเมินคะแนนของ State จะเลือกใช้เฉพาะคะแนนจาก State ที่มีคะแนนมากที่สุดจาก State ทั้งหมดที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับ State นี้
โค้ดที่ใช้เลือกและคำนวณคะแนน
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | for keys , value in dictScore.items(): print("score_calculate get keys : {} get value : {} chooseScore : {}".format(keys , value, chooseScore)) if chooseStep == '0': chooseScore = value['score'] chooseStep = keys if abs(value['score']) > abs(chooseScore): chooseScore = value['score'] chooseStep = keys # print("score_calculate playas : {} get chooseStep : {} get chooseScore : {}".format(playas, chooseStep , chooseScore)) currentScore = chooseScore * self.discount # currentStep = chooseStep self.state_action[currentStep]['score'] = currentScore self.state_action[currentStep]['end'] = False print("score_calculate playas : {} get currentStep : {},\tcurrentScore : {:7.4f},\tstepIsEnd : {}".format(playas, currentStep , currentScore , stepIsEnd)) self.dictEdgeScore[currentStep] = currentScore |
การตัดสินใจจากคะแนนของแต่ละ State
ตัว Machine จะเลือก State ไว้ 2 State คือ State ที่มี Score สูงที่สุด และมี Score น้อยที่สุด เพื่อใช้ให้เหมาะสมสำหรับทั้ง กรณีที่เล่นทั้ง X และ O ซึ่งหลังจากได้ Score มากที่สุด และน้อยที่สุดแล้ว จึงค่อยนำมาใช้ในกรณีที่เล่นเป็น X หรือ O
โค้ดในส่วนที่หา Score น้อยที่สุด และมากที่สุด
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | listStep = list(self.state_action[currentStep]['next']) # print("find_nextPlay currentStep : {} get listStep : {}".format(currentStep,listStep)) for stp in listStep: print("score_calculate get stp : {} score : {}".format(stp, self.state_action[stp]['score'])) if self.state_action[stp]['score'] < tempMinScore: tempMinScore = self.state_action[stp]['score'] tempMinStep = stp if self.state_action[stp]['score'] > tempMaxScore: tempMaxScore = self.state_action[stp]['score'] tempMaxStep = stp |
โค้ดส่วนการเลือก State ในการเล่น ที่เหมาะสมกับ State ในปัจจุบัน
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | if playas > 0: # if (tempMinStep == '0') and (tempMaxStep != '0'): if tempMaxScore > 0: print("find_nextPlay tempMaxStep : {} get tempMaxScore : {}".format(tempMaxStep,tempMaxScore)) tempStep = tempMaxStep tempScore = tempMaxScore playInvert = False else: print("No find_nextPlay tempMaxStep : {} get tempMaxScore : {}".format(tempMaxStep,tempMaxScore)) tempStep, tempScore, playInvert = self.find_Play(tempMinStep,playas*(-1)) playInvert = True if playas < 0: # if (tempMaxStep == '0') and (tempMinStep != '0'): if tempMinScore < 0: print("find_nextPlay tempMinStep : {} get tempMinScore : {}".format(tempMinStep,tempMinScore)) tempStep = tempMinStep tempScore = tempMinScore playInvert = False else: print("No find_nextPlay tempMinStep : {} get tempMinScore : {}".format(tempMinStep,tempMinScore)) tempStep, tempScore, playInvert = self.find_Play(tempMaxStep,playas*(-1)) playInvert = True print("find_nextPlay currentStep : {} get PlayStep : {} , playInvert : {}".format(currentStep,tempStep,playInvert)) |
โค้ดฟังก์ชันการเลือกเล่น
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 | def find_Play(self , currentStep = None , playas = -1): tempMinScore = 1 tempMinStep = '0' tempMaxScore = -1 tempMaxStep = '0' tempScore = 0 tempStep = '0' playInvert = False listStep = list(self.state_action[currentStep]['next']) # print("find_nextPlay currentStep : {} get listStep : {}".format(currentStep,listStep)) for stp in listStep: print("score_calculate get stp : {} score : {}".format(stp, self.state_action[stp]['score'])) if self.state_action[stp]['score'] < tempMinScore: tempMinScore = self.state_action[stp]['score'] tempMinStep = stp if self.state_action[stp]['score'] > tempMaxScore: tempMaxScore = self.state_action[stp]['score'] tempMaxStep = stp if playas > 0: # if (tempMinStep == '0') and (tempMaxStep != '0'): if tempMaxScore > 0: print("find_nextPlay tempMaxStep : {} get tempMaxScore : {}".format(tempMaxStep,tempMaxScore)) tempStep = tempMaxStep tempScore = tempMaxScore playInvert = False else: print("No find_nextPlay tempMaxStep : {} get tempMaxScore : {}".format(tempMaxStep,tempMaxScore)) tempStep, tempScore, playInvert = self.find_Play(tempMinStep,playas*(-1)) playInvert = True if playas < 0: # if (tempMaxStep == '0') and (tempMinStep != '0'): if tempMinScore < 0: print("find_nextPlay tempMinStep : {} get tempMinScore : {}".format(tempMinStep,tempMinScore)) tempStep = tempMinStep tempScore = tempMinScore playInvert = False else: print("No find_nextPlay tempMinStep : {} get tempMinScore : {}".format(tempMinStep,tempMinScore)) tempStep, tempScore, playInvert = self.find_Play(tempMaxStep,playas*(-1)) playInvert = True print("find_nextPlay currentStep : {} get PlayStep : {} , playInvert : {}".format(currentStep,tempStep,playInvert)) return tempStep , tempScore , playInvert |
ฟังก์ชันสำหรับใช้งาน
เพื่อให้สามารถเรียกใช้งานได้ง่าย จึงควรรวมฟังก์ชันการคิดคะแนน และการเลือกเล่นไว้รวมกัน รวมถึงทำให้ค่าที่ได้จากฟังก์ชันเหมาะสมกับการทำงานของระบบเกม ทำให้ไม่ต้องแก้ระบบเกมให้มารองรับฟังก์ชันของ Machine โดยเฉพาะ
โค้ดส่วนการตรวจสอบช่องว่างที่สามารถเล่นได้
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | for pos in range(len(state)): if state[pos] == 0: aval_block.append(pos+1) print("find_bestPlay get aval_block : {}".format(aval_block)) left_block = list(aval_block) operateState = self.stepList[-1] print("find_bestPlay playas : {} - get operateState : {}".format(playas,operateState)) |
โค้ดส่วนของการคิดคะแนนและการหา State ที่เหมาะสมในการเล่น
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | byStep , stepScore , status = self.score_calculate(operateState , playas) byStep , stepScore , playasStatus = self.find_Play(operateState , playas) print("find_bestPlay Step : {},\tScore : {:7.4f},\tplayasStatus : {}".format(byStep , stepScore , playasStatus)) # print("find_bestPlay get self.listEdge : {}".format(self.listEdge)) # print("find_bestPlay get self.dictEdgeScore : {}".format(self.dictEdgeScore)) # to show State by relation # self.generateGraph() |
โค้ดส่วนของการตรวจสอบ State และหาช่องว่างที่เหมาะสมในการเล่น
เริ่มที่ตรวจสอบว่าตำแหน่งที่ต้องการค้นหานั้นจะมีค่าเป็น -1 หรือ 1
1 2 | if playasStatus : playas *= (-1) |
ค้นหาดูว่าตำแหน่งที่ว่างอยู่นั้น มีค่าที่ต้องการอยู่หรือไม่
1 2 3 4 5 6 | for pos in aval_block: # print("find_bestPlay get pos {} of nextState : {} playas : {}".format(pos , nextState[pos-1] , playas)) if nextState[pos-1] == playas: play_block = pos print("find_bestPlay Predict play_block : {}".format(play_block)) break |
ถ้าหากว่าตำแหน่งนั้นเล่นได้ ก็จะใช้ค่าตำแหน่งนั้นในการเล่น
แต่หากว่าตำแหน่งนั้นไม่พร้อมที่จะให้เล่นได้ ก็จะเปลี่ยนไปค้นหาด้วยค่าของฝั่งตรงข้ามแทน
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | if play_block == 0: for pos in aval_block: # print("find_bestPlay get pos {} of nextState : {} playas : {}".format(pos , nextState[pos-1] , playas)) if nextState[pos-1] == playas*(-1): play_block = pos print("find_bestPlay Predict play_block : {}".format(play_block)) break |
แต่หากว่ายังคงไม่พบตำแหน่งที่ควรจะเล่น Machine จะทำสุ่มเล่นจากตำแหน่งที่เล่นได้
1 2 3 | if play_block == 0: play_block = random.choice(left_block) print("find_bestPlay random play_block : {}".format(play_block)) |
โค้ดฟังก์ชันใช้งาน
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 | def find_bestPlay(self , state = None , playas = -1): aval_block = [] left_block = [] play_block = 0 nextState = [] self.listEdge = [] self.dictEdgeScore = {} if state == None: return 0 for pos in range(len(state)): if state[pos] == 0: aval_block.append(pos+1) print("find_bestPlay get aval_block : {}".format(aval_block)) left_block = list(aval_block) operateState = self.stepList[-1] print("find_bestPlay playas : {} - get operateState : {}".format(playas,operateState)) byStep , stepScore , status = self.score_calculate(operateState , playas) byStep , stepScore , playasStatus = self.find_Play(operateState , playas) print("find_bestPlay Step : {},\tScore : {:7.4f},\tplayasStatus : {}".format(byStep , stepScore , playasStatus)) # print("find_bestPlay get self.listEdge : {}".format(self.listEdge)) # print("find_bestPlay get self.dictEdgeScore : {}".format(self.dictEdgeScore)) # to show State by relation # self.generateGraph() nextState = list(self.state_action[byStep]['state']) if playasStatus : playas *= (-1) for pos in aval_block: # print("find_bestPlay get pos {} of nextState : {} playas : {}".format(pos , nextState[pos-1] , playas)) if nextState[pos-1] == playas: play_block = pos print("find_bestPlay Predict play_block : {}".format(play_block)) break if play_block == 0: for pos in aval_block: # print("find_bestPlay get pos {} of nextState : {} playas : {}".format(pos , nextState[pos-1] , playas)) if nextState[pos-1] == playas*(-1): play_block = pos print("find_bestPlay Predict play_block : {}".format(play_block)) break if play_block == 0: play_block = random.choice(left_block) print("find_bestPlay random play_block : {}".format(play_block)) return play_block |
ฟังก์ชันสำหรับแสดงความสัมพันธ์ของ State
เพื่อให้เราสามารถเห็นภาพความสัมพันธ์ของ State ปัจจุบัน กับ State อื่นๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้องกัน รวมถึงคะแนนของแต่ละ State ได้ชัดเจนมากยิ่งขึ้น
ในส่วนนี้เราใช้ networkx เพื่อสร้างกราฟแสดงความสัมพันธ์
สร้าง G เป็นแบบ DiGraph
โดยความสัมพันธ์จะถูกเก็บไว้ในตัวแปร listEdge ที่ถูกอัพเดทในฟังก์ชัน คำนวณคะแนน score_calculate
1 2 3 4 | G = nx.DiGraph() # G.add_edges_from(self.listEdge) G.add_weighted_edges_from(self.listEdge) |
เปลี่ยน Label ของ Node ให้แสดงชื่อและคะแนนของ State
1 2 3 4 5 6 | for i in list(G.nodes()): # print("i in G.nodes : {}".format(i)) G.nodes[i]['Score'] = abs(self.dictEdgeScore[i]) dict_name[i] = "{} : {:4.3f}".format(i,self.dictEdgeScore[i]) # plt.figure(figsize =(9, 12)) H = nx.relabel_nodes(G,dict_name) |
คำนวนค่าเพื่อแสดงคะแนน บนกราฟ
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 | plt.subplot(111) print("The original Graph:") # node_color = [H.degree(v) for v in H] node_color = [5*(nx.get_node_attributes(H, 'Score')[v]) for v in H] # node colour is a list of degrees of nodes node_size = [nx.get_node_attributes(H, 'Score')[v] for v in H] # size of node is a list of population of cities # print("List of all node_size: {}".format(node_size)) edge_width = [1*H[u][v]['weight'] for u, v in H.edges()] # width of edge is a list of weight of edges # print("List of all edge_width: {}".format(edge_width)) # nx.draw_networkx(H, node_size = node_size, nx.draw_networkx(H, node_color = node_color, alpha = 0.5, # with_labels = True, width = edge_width, with_labels = True, edge_color = edge_width, cmap = plt.cm.Blues) plt.axis('off') plt.tight_layout(); # nx.draw_networkx(H, with_label = True) print("Total number of nodes: ", int(H.number_of_nodes())) print("Total number of edges: ", int(H.number_of_edges())) print("List of all nodes: ", list(H.nodes())) print("List of all edges: ", list(H.edges(data = True))) print("Degree for all nodes: ", dict(H.degree())) plt.show() |
เพื่อให้สามารถเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันนี้ได้ จะต้อง เอาคอมเมนต์ของบรรนทัดนี้ออกไปเสียก่อน
1 2 | # to show State by relation self.generateGraph() |
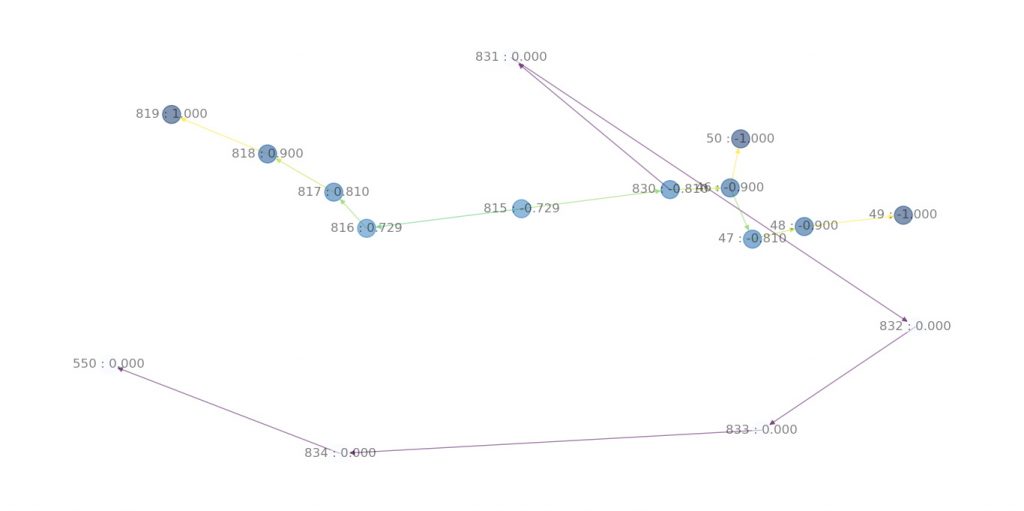
เมื่อ Machine ทำงาน ระบบจะมีการแสดงภาพความสัมพันธ์ดังตัวอย่าง
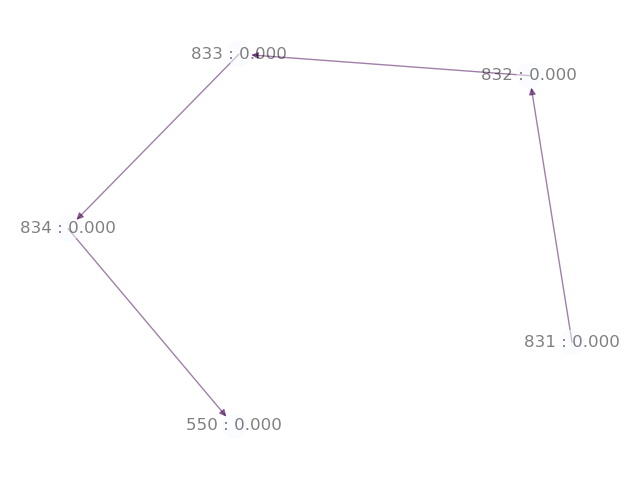
โค้ดสำหรับแสดงความสัมพันธ์ของ State
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 | def generateGraph(self): # edges = [(1, 2), (1, 6), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 6), # (3, 4), (3, 5), (4, 8), (4, 9), (6, 7)] dict_name = {} # self.generateEdge() G = nx.DiGraph() # G.add_edges_from(self.listEdge) G.add_weighted_edges_from(self.listEdge) # We have to set the population attribute for each of the 14 nodes for i in list(G.nodes()): # print("i in G.nodes : {}".format(i)) G.nodes[i]['Score'] = abs(self.dictEdgeScore[i]) dict_name[i] = "{} : {:4.3f}".format(i,self.dictEdgeScore[i]) # plt.figure(figsize =(9, 12)) H = nx.relabel_nodes(G,dict_name) # original Graph created # print("List of H nodes: {}".format(H.nodes())) plt.subplot(111) print("The original Graph:") # node_color = [H.degree(v) for v in H] node_color = [5*(nx.get_node_attributes(H, 'Score')[v]) for v in H] # node colour is a list of degrees of nodes node_size = [nx.get_node_attributes(H, 'Score')[v] for v in H] # size of node is a list of population of cities # print("List of all node_size: {}".format(node_size)) edge_width = [1*H[u][v]['weight'] for u, v in H.edges()] # width of edge is a list of weight of edges # print("List of all edge_width: {}".format(edge_width)) # nx.draw_networkx(H, node_size = node_size, nx.draw_networkx(H, node_color = node_color, alpha = 0.5, # with_labels = True, width = edge_width, with_labels = True, edge_color = edge_width, cmap = plt.cm.Blues) plt.axis('off') plt.tight_layout(); # nx.draw_networkx(H, with_label = True) print("Total number of nodes: ", int(H.number_of_nodes())) print("Total number of edges: ", int(H.number_of_edges())) print("List of all nodes: ", list(H.nodes())) print("List of all edges: ", list(H.edges(data = True))) print("Degree for all nodes: ", dict(H.degree())) plt.show() |
Library ที่ใช้
สามารถติดตั้งจากไฟล์ text โดยใช้คำสั่ง pip install -r <ชื่อไฟล์> ได้
ในไฟล์ text นั้นมีเนื้อหาดังนี้
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | astroid ==2.3.3 certifi ==2019.9.11 colorama ==0.4.1 cycler ==0.10.0 decorator ==4.4.1 isort ==4.3.21 kiwisolver ==1.1.0 lazy-object-proxy ==1.4.3 matplotlib ==3.1.2 mccabe ==0.6.1 networkx ==2.4 numpy ==1.17.4 pip ==19.3.1 pylint ==2.4.4 pyparsing ==2.4.5 python-dateutil ==2.8.1 setuptools ==41.6.0.post20191030 six ==1.13.0 wheel ==0.33.6 wincertstore ==0.2 wrapt ==1.11.2 |
การใช้งาน
ระบบจะมีไฟล์ประกอบด้วยกัน 4 ไฟล์คือ
- main.py
- markovDT.py
- state_action.json
- requirement.txt
เริ่มต้นด้วยเรียกคำสั่ง python เพื่อรันไฟล์ main.py
1 | (pyGames) C:\Users\Jaa\Desktop\tictactoe>python -m main |
เลือกว่าจะเริ่มเล่นก่อนหรือไม่
เริ่มเล่นเกม
Machine ประมวลผล และเลือกวาง O ลงในตำแหน่งที่ 5
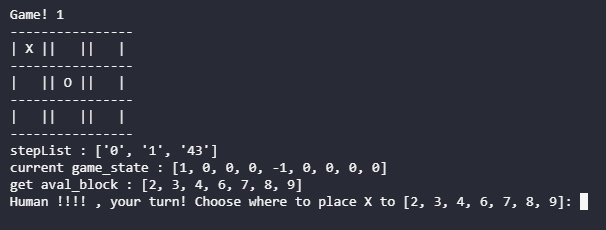
เล่นแบบนี้ไปจนจบเกมส์
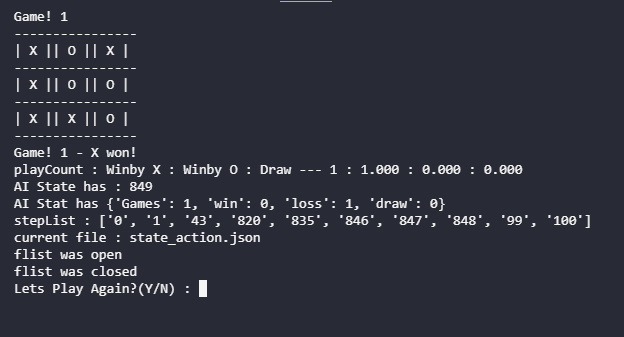
เมื่อเกมสิ้นสุดลง จะมีคำถามให้เลือกว่าจะเล่นต่ออีกหรือไม่
ไฟล์ที่ใช้
ไฟล์ทั้งหมดสามารถ Download ได้ที่ https://github.com/playelek/Tik-Tak-Toe.git
ไฟล์ state_action.json จะเป็นไฟล์ว่างเปล่า ซึ่งจะเอาไว้เก็บ State
สรุป
ทั้งหมดนี้ทำขึ้นเพียงเพื่อทดลอง และใช้เล่นสนุกๆเท่านั้น
และยังมีช่องว่างให้ถูกพัฒนาต่อได้อีกมาก เช่นการใช้ประโยชน์จากความสมมาตรของตาราง ที่สามารถหมุนตารางก่อน แล้วค่อยนำมาเปรียบเทียบ หรือการทำ Mirror ตาราง ก่อนจะนำมาเปรียบเทียบ ซึ่งจะทำให้รูปแบบของเกมลดลงไปอย่างมาก
นอกจากนี้ตัว Machine ยังเปิดช่องให้สามารภนำเอาเทคนิคอื่นๆมาปรับใช้ได้อีกด้วย เช่นการใช้ Neural Network มาแทน ก็สามารถทำได้ ซึ่งถ้ามีโอกาสจะลองทำมาแบ่งปันกันอีกครั้ง
อ้างอิง
minimax
https://stackabuse.com/minimax-and-alpha-beta-pruning-in-python/
https://towardsdatascience.com/create-ai-for-your-own-board-game-from-scratch-minimax-part-2-517e1c1e3362
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/minimax-algorithm-in-game-theory-set-1-introduction/
https://dev.to/nestedsoftware/tic-tac-toe-with-the-minimax-algorithm-5988
networkx
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/operations-on-graph-and-special-graphs-using-networkx-module-python/
https://towardsdatascience.com/python-interactive-network-visualization-using-networkx-plotly-and-dash-e44749161ed7
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ml-reinforcement-learning-algorithm-python-implementation-using-q-learning/
